Light, Color, and Electromagnetic Radiation
Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that has wave-like and particle-like behavior as it travels through space.
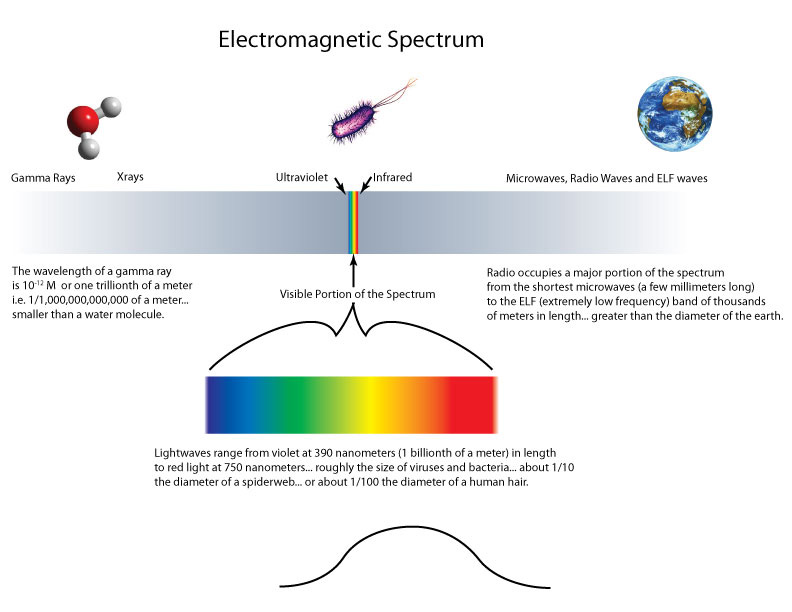
The electromagnetic spectrum consists of radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, gamma rays, etc.
Electromagnetic radiation can be characterized by its wavelength...
There is a broad range of wavelengths in the Electromagnetic spectrum.
There is a narrow range of this electromagnetic energy from the sun and other light sources which creates energy of wavelengths visible to humans. These wavelengths are so small, they are measured in nanometers. The average human hair is 50,000 to 60,000 nanometers in diameter. There are 25,400,000 nm per 1 inch.
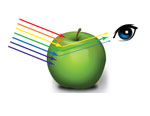
Each of these wavelengths, from approximately 390 nm to 750 nm, is associated with a particular color response. For example, the wavelengths near 400 nm are violet in color while those near 700 nm are red.
When the wavelength is within the visible spectrum (the range of wavelengths humans can perceive,
approximately from 390 nm to 750 nm), it is known as "visible light."
Color
Color is the property possessed by an object producing different sensations on the eye and in the brain as a result of the way it reflects, transmits or emits light.
Light Sources
Most light sources emit light at many different wavelengths. As you can see in the images below, different light sources have different gamuts and will affect the appearance of a work. |
||
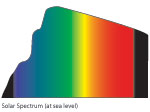
| If the Sun is the light source, the range of light is known as the Visible Solar Spectrum. The graph shows the relative strength of different wavelengths (colors) of light from the Sun. |
The black ares on either |
 |
| This is the relative color output of an incandescent lamp | 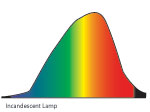 |
 |
| The so-called Full Spectrum fluorescent lamp has high "spikes" in several areas. | 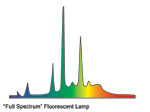 |
 |
| This is the output of a "white" LED lamp | 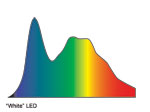 |
 |
| Not only do the colors of paint (the local color) affect how we see something, the color of the light hitting the object also influences our view. Click here for all four Vermeer variations. | ||
HUES, Primary, Secondary and Tertiary
Hue is the common name of a pure color. Hue is one of the three qualities that may be used to describe any color. Hue defines a pure color in terms like "red", "green", "blue-violet".
Primary colors are sets of colors that can be combined to make a useful range of colors. Three primary colors are usually used and, with the addition of white, THEORETICALLY, can be mixed to create all other colors.
When two Primary colors are mixed in equal amounts, the resulting color is a Secondary color.
In some color systems, an additional standardized mix is included: Tertiary Colors... the equal mixing mixing of a primary and one of its two closest secondaries.
COLOR MODELS (also known as Color Systems)
| A color model Or color system) is a way to describe colors based on certain characteristics such the color's Red, Green and Blue levels... or its hue, brightness, saturation, etc. | |
For example, in one color model, this color has red, green and blue levels of 83, 185 and and 74 respectively... And, in a different color model, it has a hue of 114 degrees, a brightness of 73% and a saturation of 61%. It's the same color... just described by a different color model. |
 |
There are two basic Color Models, additive and subtractive, each of which have a variety of sub-models.
These two models differ based on the source of the light.
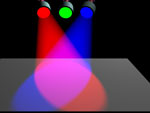
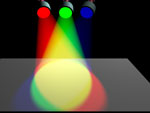
Additive Color System
If the color that you see is coming directly from a light source, such as light from a spotlight, computer monitor, or television,
the system of color mixing is called additive. Light can be added to create various colors.
The more colors of light you add, the lighter, brighter and whiter (depending upon the hues added) it gets.
Additive Color System
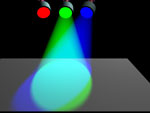
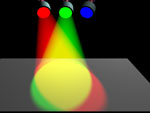
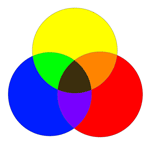
| In the additive color system, the three primaries are Red, Green and Blue. | |
| If these three colors of light are equally mixed together, they will produce what appears to be white light. | 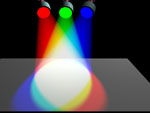 |
Subtractive Color System
If the color that you see is caused by light reflected and/or absorbed by the surface of an object (and NOT coming directly from a light source),
the system of color mixing is called subtractive.
As with the additive color system, there are primary and secondary subtractive colors.
And, as with the additive color system,when two subtractive primaries are equally mixed, they produce a secondary color.
BUT, unlike the additive color system, with its RGB primaries, there are different sets of subtractive primary colors... the set most commonly used by artists is the traditional pigment color system
NOTE: Any three "primary" colors of light, paint, ink, etc. can mix only a limited range of colors, called a gamut, which is always smaller (contains fewer colors) than the full range of colors humans can perceive.
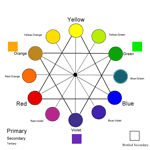
The Traditional Pigment Color Wheel
A color wheel is the visible spectrum bent into a circle. The Color Wheel shows the relationships between colors. It is laid out so that any two PRIMARY COLORS (red, yellow, blue) are separated by a SECONDARY COLORS (orange, violet, and green).
There are three primary colors; red, blue, and yellow. Primary colors are hues which THEORETICALLY can be mixed (with the addition of white) to create all other colors.
There are three secondary colors; green, orange, and violet. Secondary colors are the hues between the primary hues on the color wheel. The secondary hues are created by mixing two primary hues in equal amounts. To get orange, you mix equal parts of red and yellow. To get Violet, you mix equal parts of red and blue. To get green, you mix equal parts of blue and yellow.
There are also tertiary colors... third order colors... made by mixing a secondary with an equal amount of one of its neighboring primaries.
Assignment
Traditional Pigment color wheel of 12 colors made with ONLY 3 colors of paint… RED, YELLOW and BLUE
- Paint the 12 colors using ONLY the primaries (You must mix the secondaries and tertiaries from the primaries)... e.g., do NOT use orange paint... instead, mix it from red and yellow, etc.
- Paint the 12 colors in even steps
- Indicate primaries, secondaries and tertiaries
- Use color patches that are larger than 1 square inch in area
- Neatly cut out the patches of color (at least 1 square inch in area)
- You may be inventive with the shapes of each color, but each sample should be approximately square inch in area.
- Arrange the colors based on the six-pointed star format
- Glue in place
- Include a sample of the 3 pure, out of the tube, bottle, etc. secondaries near the mixed secondaries (at least 1 square inch in area)
- Title the color wheel "Traditional Pigment Color Wheel"
- Label or provide a key to the Primary, Secondary, Tertiary and bottled secondary colors
- Label the individual hues... "Red," "Red-Orange," etc.
Craft counts MUCHO!
Sample color wheels. Note... Because these wheels were made on a computer, the colors are not accurate examples of paint colors. Use these for shape/layout ideas only. |
 |
 |
 |