More on Perspective
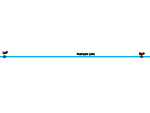
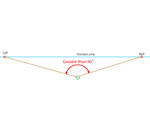
The horizon line is a theoretical line that represents the eye level of the observer. The horizon line is the same as the landscape's horizon; however, most of the time, hills, trees, buildings, and other objects obscure the horizon. Usually the horizon is not visible indoors, but there is still a theoretical horizon line representing the eye level of the observer.
Two-point linear perspective:There are three kinds of lines used in two-point perspective...
|
Drawing Boxes in Two-point Linear Perspective |
|
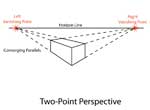 |
|
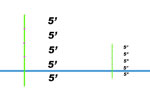
| Establish a horizon line |  |
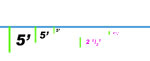
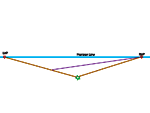
| Draw the nearest corner of the box as a vertical line to the height you want the box to be. | 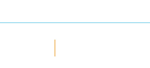 |
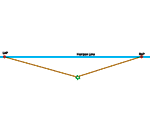
| Establish a left and a right vanishing point. | 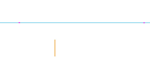 |
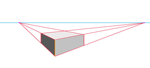
| Connect the bottom of the box to the right and left vanishing points... be sure the angle between the two orthogonals is greater than 90 degrees. If it isn't, move one or both of the vanishing points further from the center, and redraw the orthogonal(s). | 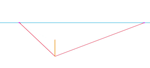 |
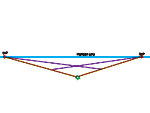
| Connect the top of the nearest corner of the box to the right and left vanishing points. | 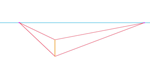 |
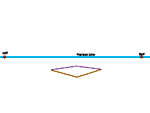
| Draw a vertical line between the two converging right-side lines. | 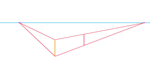 |
| Connect the top of it to the left vanishing point. | 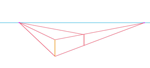 |
| Draw a vertical line between the two converging left-side lines. | 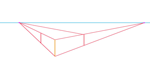 |
| Connect it to the right vanishing point. | 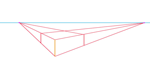 |
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
Canaletto |
Salvador Dali, Crucifix |
|
Edward Hopper |
Edward Hopper |
 |
Temple_of_Concord |
|
Thomas Mundy Peterson School (In additon to being the first black man to vote in America (March 31, 1870), Peterson was also the Perth Amboy, NJ's first African American to serve on a jury and the first black man in Middlesex County, New Jersey to hold elected office.) |
|
Assignments
- draw a two point box located below the horizon line,
- one hovering above the horizon, and
- one that is about halfway above and below the horizon.
- Photograph, printout, and mount in sketchbook, examples of 2-point perspective (at least 4).
|
 |